What Is a Software-Defined Vehicle?
A software-defined vehicle is any vehicle that manages its operations, adds functionality, and enables new features primarily or entirely through software.
Software-defined vehicles are the next evolution of the automotive industry. They are the foundation of many other advancements, including self-driving and connected cars. Deloitte notes that they ultimately reflect “the gradual transformation of automobiles from highly electromechanical terminals to intelligent, expandable mobile electronic terminals that can be continuously upgraded”.
Benefits of Software-Defined Vehicles
The benefits of software-defined vehicles include:
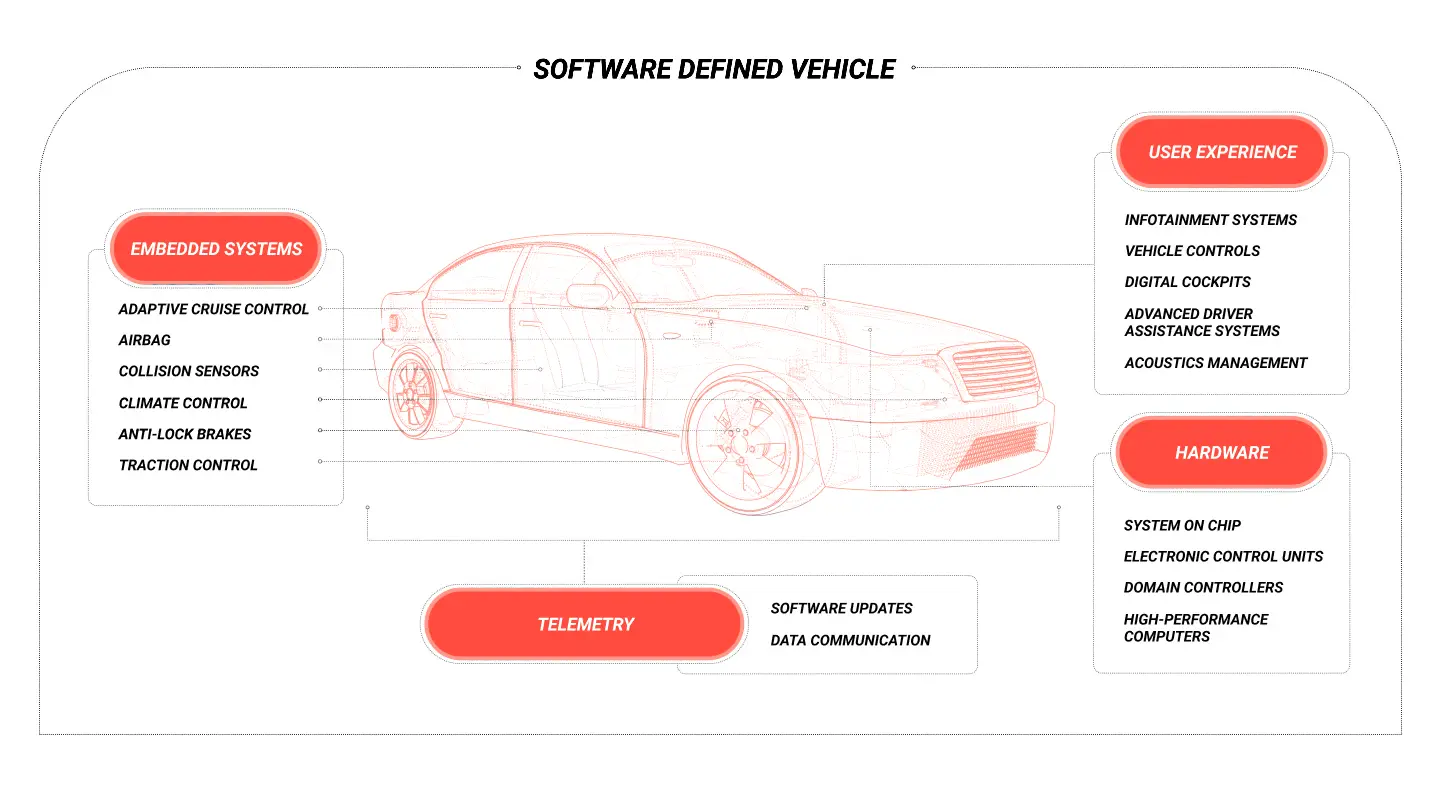
- Improved safety via features such as anti-collision systems and driver assistance
- Increased comfort through onboard infotainment systems that integrate connected features such as music and video streaming
- Deeper insights into vehicle performance through telematics and diagnostics, allowing for more effective preventative maintenance
- The capacity for automotive manufacturers to add new features and functionality with over-the-air updates
Software-defined vehicles outperform their hardware-defined predecessors across multiple arenas. In addition to being safer, they provide superior comfort and convenience. Since many Software-defined vehicles are also electric, they could have considerably smaller environmental footprints.
Optimization is another major draw. Manufacturers can continue improving the driver experience and enhance vehicle performance after a car leaves the factory, perpetually improving the driving experience through ongoing development. This represents the most significant paradigm shift the automotive industry has ever experienced, as hardware-defined cars tend to remain generally unchanged throughout their lifecycles.
More Benefits of Software-Defined Vehicles
- Increased value of the vehicle over time as new features are added via software updates
- Connectivity between vehicle and smartphone, allowing drivers and passengers to interact with their cars in new ways
- Continuous connectivity, delivering real-time information services to and from the vehicle
Software-Defined Vehicle Architecture
1. User Applications
2. Instrumentation
3. Embedded OS
4. Hardware
Software-Defined Vehicles vs. Connected Vehicles
There is very little difference between software-defined vehicles and connected vehicles.
Both are characterized by extensive safety, convenience, and entertainment features provided and enabled through onboard software. Both integrate multiple software services and platforms through either middleware or APIs. Both incorporate various advanced hardware such as collision detection and ADAS.
The only tangible difference is that, in theory, connected cars have a slightly different use case, explicitly built to interact and interface with their surroundings. Given that many Software-Defined Vehicles now share this functionality, the two are essentially indistinguishable from one another.
A smart city is one that’s capable of harnessing the power of today’s most innovative technologies. These cities are defined as urban areas that utilize information and communication technologies (ICT) to improve government services and make them more efficient. Smart cities can also improve the flow and function of how drivers navigate through the urban environment.
As the smart city moves from concept to reality, the SDV will become even more important as a dynamic node in this system. In the smart city, data and information technology are leveraged to improve operational efficiency, share services with public citizens, and provide a better quality of government. This includes helping traffic flow more smoothly, imposing environmental regulations, managing parking more effectively, and reducing energy usage where possible. SDVs will facilitate the integration of vehicles into the smart city.
Software Defined Vehicles and Vehicle-to-Everything
Connectivity is central to the concept of the software-defined vehicle. Updating features over the air and providing drivers with live information during their journeys are vital capabilities. The SDV is also integral to realizing Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technology. With V2X, the information flow between the car and its surroundings is constant and two-way.
V2X enables vehicles to benefit from urban smart city Internet of Things sensors and data while contributing information from its sensors to central repositories. With SDVs, V2X technology is much easier to implement. The integration of vehicle systems that SDVs provide via software stacks and standards-based communication methods will be a hub for V2X.
Closely linked to smart city developments, V2X leverages high-bandwidth, low-latency wireless connectivity such as 5G to enhance vehicle safety using data supplied by the environment. It can also facilitate driver services, including automatic payment when entering restricted urban areas such as parking or controlled zones, and provide information to other drivers.
Software Defined Vehicles and Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are primarily a software challenge. While a self-driving hardware system relies on a suite of different sensors, including cameras, radar, LiDAR, and others, what enables autonomy are sophisticated road behavior models developed using intensive Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) processed on some of the most powerful supercomputers in the world.
Once implemented, an autonomous driving system requires complete control over core driving functions like acceleration, braking, and steering. This can only be delivered when these functions are interconnected via a central computer running software that integrates them. The SDV provides this with its focus on software as the primary method for delivering functionality.
Full self-driving will also likely require regular software updates as new capabilities and safety improvements become available. The SDV enables this, especially as fewer and fewer features rely on fixed hardware platforms and ECUs that cannot be upgraded dynamically.
Software Defined Vehicles and Cybersecurity
To compromise vehicles without connectivity, threat actors need physical access—they need to be near the car when keyless entry is invoked or be in a location with both the car and its keys in the vicinity. For deeper levels of compromise, they would need to enter the vehicle to connect to the diagnostics port.
With an SDV, these functions could be accessed remotely, similar to the malware attacks perpetrated on personal devices and corporate systems. Although there have been no publicized incidents of this occurring (except for controlled demonstrations), the mission-critical nature and safety requirements of road vehicles mean that a breach could be more immediately serious than the theft of even bank details: A moving car suddenly losing its ADAS functions because of a cyberattack could be life-threatening. A compromised self-driving vehicle could be turned into a weapon.
This is why a vehicle software platform with a strong cybersecurity pedigree, such as QNX®, will be essential as SDVs gain popularity. Vehicle software must implement proactive protection systems against cyberattacks like corporate network systems. Cybersecurity solutions can recognize and nullify existing known attacks and detect behavior that could be a previously unseen attempt to compromise systems. With SDVs employing powerful computing hardware, this can be leveraged to run AI-enhanced cybersecurity, keeping vehicles secure and their occupants safe.
FAQ
What is a software-defined vehicle?
A software-defined vehicle manages operations and enables new features and functionality almost entirely through onboard software.
What software is used in the automotive industry?
QNX is a market leader in automotive software, embedded in more than 235 million vehicles worldwide. The platform’s leadership is expected to persist through 2026. Other significant players in the space include Android, Linux, and Windows Embedded Automotive.
What’s the difference between a software-defined vehicle and a connected vehicle?
In theory, connected cars are built specifically to interact with IoT devices in their surroundings. However, in practice, there is very little difference between the two as SDVs generally provide the same functions and they are used mainly to reference the same concepts.
Is Tesla a software-defined vehicle?
Tesla first popularized the concept of software-defined vehicles in 2012. The company remains one of the best-known brands in the space to this day. However, many other manufacturers are now realizing the need for a software-first approach to their vehicle platforms.
What’s the connection between software-defined vehicles and self-driving vehicles?
Software-defined vehicles essentially lay the foundation for self-driving cars. Many safety features in software-defined vehicles, such as sensors and LiDAR, are also crucial for autonomous driving.
As the developer of QNX®, we are one of the leading organizations in the Software-Defined Vehicle space. For more than forty years, we’ve worked tirelessly to build safe, reliable, and secure embedded systems. And we’re not stopping there—in addition to investing heavily in autonomous vehicle research, we’re also working to enable the connected car.
That’s where IVY® comes in. Leveraging QNX, edge computing, and the cloud, IVY empowers developers and automakers with a secure, reliable way to share vehicle data, deliver new features and functionality, and fuel innovation. IVY is compatible with most platforms and shares close ties with BlackBerry’s broad development community.
Check Out Our Other Ultimate Guides




